GESIS Search is a service by GESIS - Leibniz Institute for the Social
Sciences to look up information about research data, survey variables,
empirical instruments and tools, literature, and library collections
from the social sciences. rgesis is a package to query its
search engine to retrieve metadata on search records and to download
survey data from GESIS’ comprehensive data archive. It does so in a
reproducible manner that can easily be embedded in code files and
publications. The package mainly consists of three functions
- Authenticate a session using
gesis_auth() - Search the GESIS catalogue using
gesis_search() - Retrieve data using
gesis_data()
Authentication
GESIS expects all users who wish to download a data file to be logged
in. The gesis_auth() function takes over this task purely
programmatically. You need to provide the function with a user email and
a password. The credentials are used to login once and then stored in a
secure keyring storage. If you
get a success message, you are good to go.
gesis_auth(email = "jonas.lieth@gesis.org", password = "****")
# ✔ Successfully performed GESIS login.You can also manually check the stored credentials by interacting with the keyring.
keyring::key_list("rgesis")
#> service username
#> 1 rgesis jonas.lieth@gesis.orgGESIS Search
Even without authentication, you can use rgesis to
retrieve metadata on GESIS search entries like datasets, variables,
publications or tools. This can be done using the
gesis_search() function which offers tools for querying and
filtering the GESIS search engine. For example, to get metadata on the
German General Social Survey (ALLBUS) from 2018, you can do:
gesis_search(
"allbus",
type = "research_data",
collection_year = c(2018, 2018)
)
#> A list of <gesis_records> with 10 records
#> <gesis_record>
#> Type: research_data
#> ID: ZA5270
#> Title: Allgemeine Bevölkerungsumfrage der Sozialwissenschaften ALLBUS 2018
#> Date: 2019
#> Persons:
#> • Diekmann, Andreas
#> • Hadjar, Andreas
#> • Kurz, Karin
#> • Rosar, Ulrich
#> • Wagner, Ulrich
#> • ... and 1 more
#>
#> <gesis_record>
#> Type: research_data
#> ID: ZA5272
#> Title: German General Social Survey - ALLBUS 2018
#> Date: 2019
#> Persons:
#> • Diekmann, Andreas
#> • Hadjar, Andreas
#> • Kurz, Karin
#> • Rosar, Ulrich
#> • Wagner, Ulrich
#> • ... and 1 more
#>
#> <gesis_record>
#> Type: research_data
#> ID: ZA5260
#> Title: Allgemeine Bevölkerungsumfrage der Sozialwissenschaften - ALLBUS
#> Sensitive Regionaldaten
#> Date: 2021
#> Persons:
#> • Allerbeck, Klaus
#> • Allmendinger, Jutta
#> • Andreß, Hans-Jürgen
#> • Bürklin, Wilhelm
#> • Diekmann, Andreas
#> • ... and 21 more
#>
#> <gesis_record>
#> Type: research_data
#> ID: ZA5274
#> Title: Allgemeine Bevölkerungsumfrage der Sozialwissenschaften ALLBUS -
#> Kumulation 1980-2018
#> Date: 2021
#> Persons:
#> • Allerbeck, Klaus
#> • Allmendinger, Jutta
#> • Andreß, Hans-Jürgen
#> • Bauernschuster, Stefan
#> • Bürklin, Wilhelm
#> • ... and 25 more
#>
#> <gesis_record>
#> Type: research_data
#> ID: ZA5276
#> Title: German General Social Survey (ALLBUS) - Cumulation 1980-2018
#> Date: 2021
#> Persons:
#> • Allerbeck, Klaus
#> • Allmendinger, Jutta
#> • Andreß, Hans-Jürgen
#> • Bauernschuster, Stefan
#> • Bürklin, Wilhelm
#> • ... and 25 more
#> # ℹ 5 more records
#> # ℹ Use `print(n = ...)` to see more records"allbus" is the query string,
"research_data" is the result type (you can also search for
other types like publications or tools), and c(2018, 2018)
is the time in which the queried dataset must be collected.
If you need this data in a more workable manner, you can set
tidy = TRUE. This will convert the metadata to a pretty
dataframe. Be aware that not all metadata fields can be fit in a
rectangular shape and must be dropped. If completeness of metadata
records is a priority, you should leave the output untidy.
gesis_search(
"allbus",
type = "research_data",
collection_year = c(2018, 2018),
tidy = TRUE
)
#> # A tibble: 10 × 105
#> id title type date study_title date_recency study_number portal_url
#> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 ZA5270 Allgemei… rese… 2019 Allgemeine… 2018 ZA5270 https://d…
#> 2 ZA5272 German G… rese… 2019 German Gen… 2018 ZA5272 https://d…
#> 3 ZA5260 Allgemei… rese… 2021 Allgemeine… 2018 ZA5260 https://d…
#> 4 ZA5274 Allgemei… rese… 2021 Allgemeine… 2018 ZA5274 https://d…
#> 5 ZA5276 German G… rese… 2021 German Gen… 2018 ZA5276 https://d…
#> 6 ZA5262 Allgemei… rese… 2021 Allgemeine… 2018 ZA5262 https://d…
#> 7 ZA5273 German G… rese… 2019 German Gen… 2018 ZA5273 https://d…
#> 8 ZA5277 German G… rese… 2021 German Gen… 2018 ZA5277 https://d…
#> 9 ZA5271 Allgemei… rese… 2019 Allgemeine… 2018 ZA5271 https://d…
#> 10 ZA5275 Allgemei… rese… 2021 Allgemeine… 2018 ZA5275 https://d…
#> # ℹ 97 more variables: person_sort <chr>,
#> # primary_researchers_advisory_board_institution <list>, subtype <chr>,
#> # abstract <chr>, source <chr>, time_collection <chr>,
#> # time_collection_max_year <chr>, time_collection_min_year <chr>,
#> # time_collection_years <list>, countries_collection <chr>,
#> # countries_iso <chr>, countries_free <chr>, countries_view <chr>,
#> # methodology_collection <chr>, analysis_system <chr>, …While the first 10 results are enough for many use cases, sometimes
you just need more than that. By default, gesis_search()
only requests the first search page. You can choose which pages to
request by setting the pages argument. You can even request
all pages by setting it to NULL.
gesis_search(
"allbus",
type = "research_data",
collection_year = c(2018, 2018),
tidy = TRUE,
pages = NULL
)
#> # A tibble: 13 × 121
#> id title type date study_title date_recency study_number portal_url
#> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 ZA5270 Allg… rese… 2019 Allgemeine… 2018 ZA5270 https://d…
#> 2 ZA5272 Germ… rese… 2019 German Gen… 2018 ZA5272 https://d…
#> 3 ZA5260 Allg… rese… 2021 Allgemeine… 2018 ZA5260 https://d…
#> 4 ZA5274 Allg… rese… 2021 Allgemeine… 2018 ZA5274 https://d…
#> 5 ZA5276 Germ… rese… 2021 German Gen… 2018 ZA5276 https://d…
#> 6 ZA5262 Allg… rese… 2021 Allgemeine… 2018 ZA5262 https://d…
#> 7 ZA5273 Germ… rese… 2019 German Gen… 2018 ZA5273 https://d…
#> 8 ZA5277 Germ… rese… 2021 German Gen… 2018 ZA5277 https://d…
#> 9 ZA5271 Allg… rese… 2019 Allgemeine… 2018 ZA5271 https://d…
#> 10 ZA5275 Allg… rese… 2021 Allgemeine… 2018 ZA5275 https://d…
#> 11 SDN-10.78… Harm… rese… 2021 Harmonizin… 2021 NA https://d…
#> 12 SDN-10.78… Harm… rese… 2021 Harmonizin… 2021 NA https://d…
#> 13 SDN-10.78… Harm… rese… 2021 Harmonizin… 2021 NA https://d…
#> # ℹ 113 more variables: person_sort <chr>,
#> # primary_researchers_advisory_board_institution <list>, subtype <chr>,
#> # abstract <chr>, source <chr>, time_collection <chr>,
#> # time_collection_max_year <chr>, time_collection_min_year <chr>,
#> # time_collection_years <list>, countries_collection <chr>,
#> # countries_iso <chr>, countries_free <chr>, countries_view <chr>,
#> # methodology_collection <chr>, analysis_system <chr>, …To exemplify, we can perform a very basic bibliographic analysis of the evolution of climate change literature based on the most relevant 5000 records in the GESIS archive.
cc <- gesis_search(
"climate change",
type = "publication",
pages = 1:500,
tidy = TRUE
)
library(ggplot2)
ggplot(na.omit(cc[c("date", "subtype")])) +
geom_bar(aes(x = date, fill = subtype)) +
scale_y_continuous(expand = c(0, 0)) +
scale_fill_discrete("Type", labels = c(
book = "Book",
in_proceedings = "Proceedings",
journal_article = "Article"
)) +
guides(x = guide_axis(check.overlap = TRUE)) +
labs(x = NULL, y = "Count") +
theme_classic()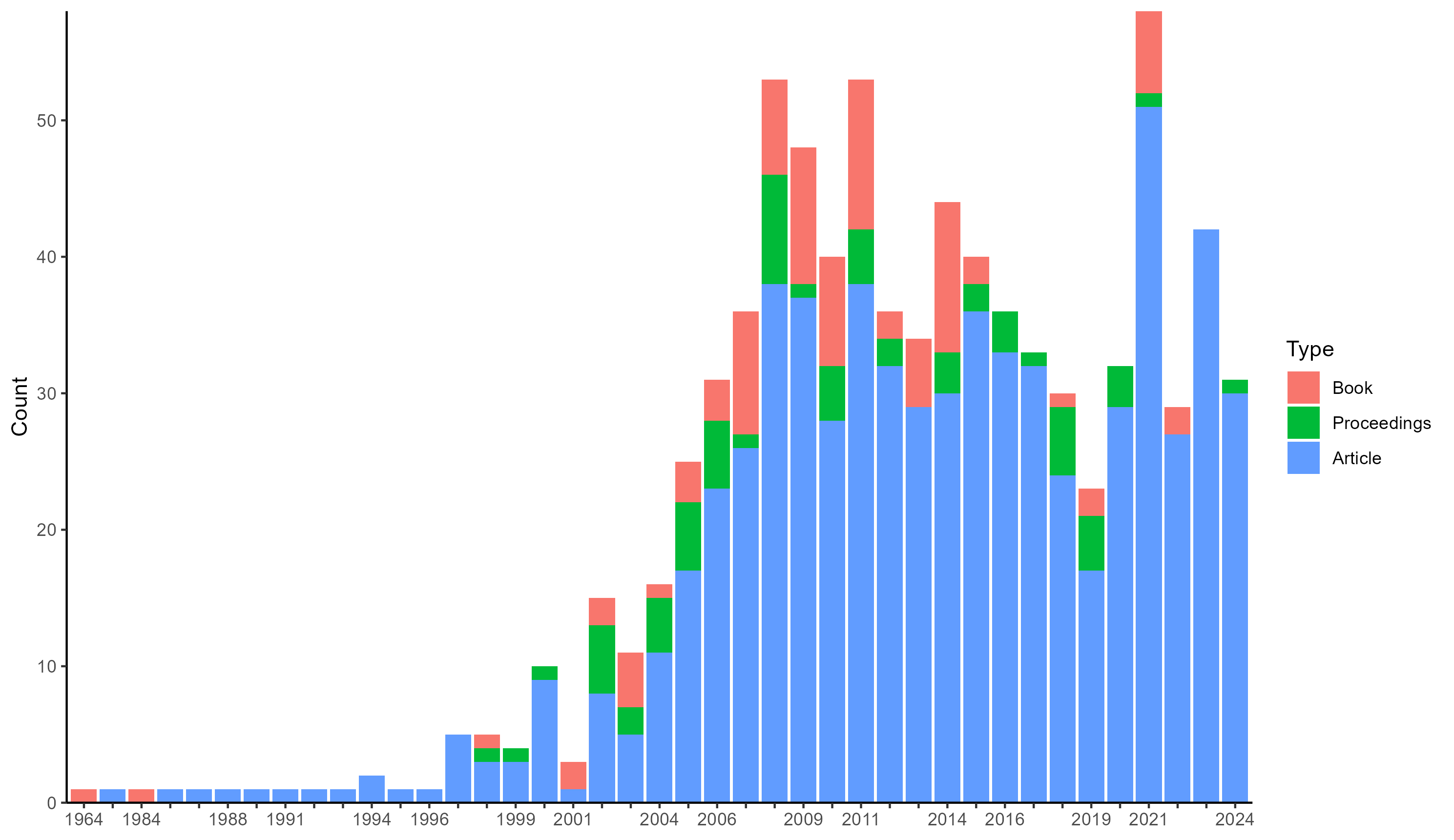
Finally, if you already know a dataset or record you want to look up,
you can use the gesis_get() function to search for a
specific record ID. These IDs can be retrieved from the metadata records
returned by gesis_search().
allbus <- gesis_get("ZA5272")
allbus
#> <gesis_record>
#> Type: research_data
#> ID: ZA5272
#> Title: German General Social Survey - ALLBUS 2018
#> Date: 2019
#> Persons:
#> • Diekmann, Andreas
#> • Hadjar, Andreas
#> • Kurz, Karin
#> • Rosar, Ulrich
#> • Wagner, Ulrich
#> • ... and 1 moreData retrieval
Both of the last two steps ultimately help to retrieve survey data
from the GESIS data archive. First, authentication is needed to be
allowed to download in the first place. Second, a metadata record (or at
least a record ID) is needed to specify what dataset you want to
download. Finally, it is often a good idea to first explore what kinds
of data are in store for a given record. The
gesis_file_types() function gives insights into the types
of data available.
gesis_file_types(allbus)
#> [1] "dataset" "questionnaire" "codebook"Now we know that the ALLBUS record contains dataset files. But which files are available exactly?
gesis_files(allbus, type = "dataset")
#> <gesis_files>
#> → File 1
#> Label: ZA5272_v1-0-0.dta.zip
#> File size: 0.94 MB
#> Login required? yes
#> ────
#> → File 2
#> Label: ZA5272_v1-0-0.sav.zip
#> File size: 1.02 MB
#> Login required? yesUsing this information, we can download the .sav file to disk using
the gesis_data() function.
path <- gesis_data(allbus, select = "\\.sav")Since GESIS files can come in all kinds of file formats, the package leaves reading the data to the user. In this case, we can use the haven package to read the downloaded file.
library(dplyr)
library(stringr)
library(haven)
allbus_data <- read_sav(path)
allbus_data <- allbus_data |>
select(eastwest, economic_situation = ep01, samesex_marriage = pa12) |>
mutate(across(everything(), .fns = ~as_factor(.x))) |>
mutate(eastwest = str_to_title(eastwest)) |>
select(economic_situation, samesex_marriage, eastwest) |>
na.omit()
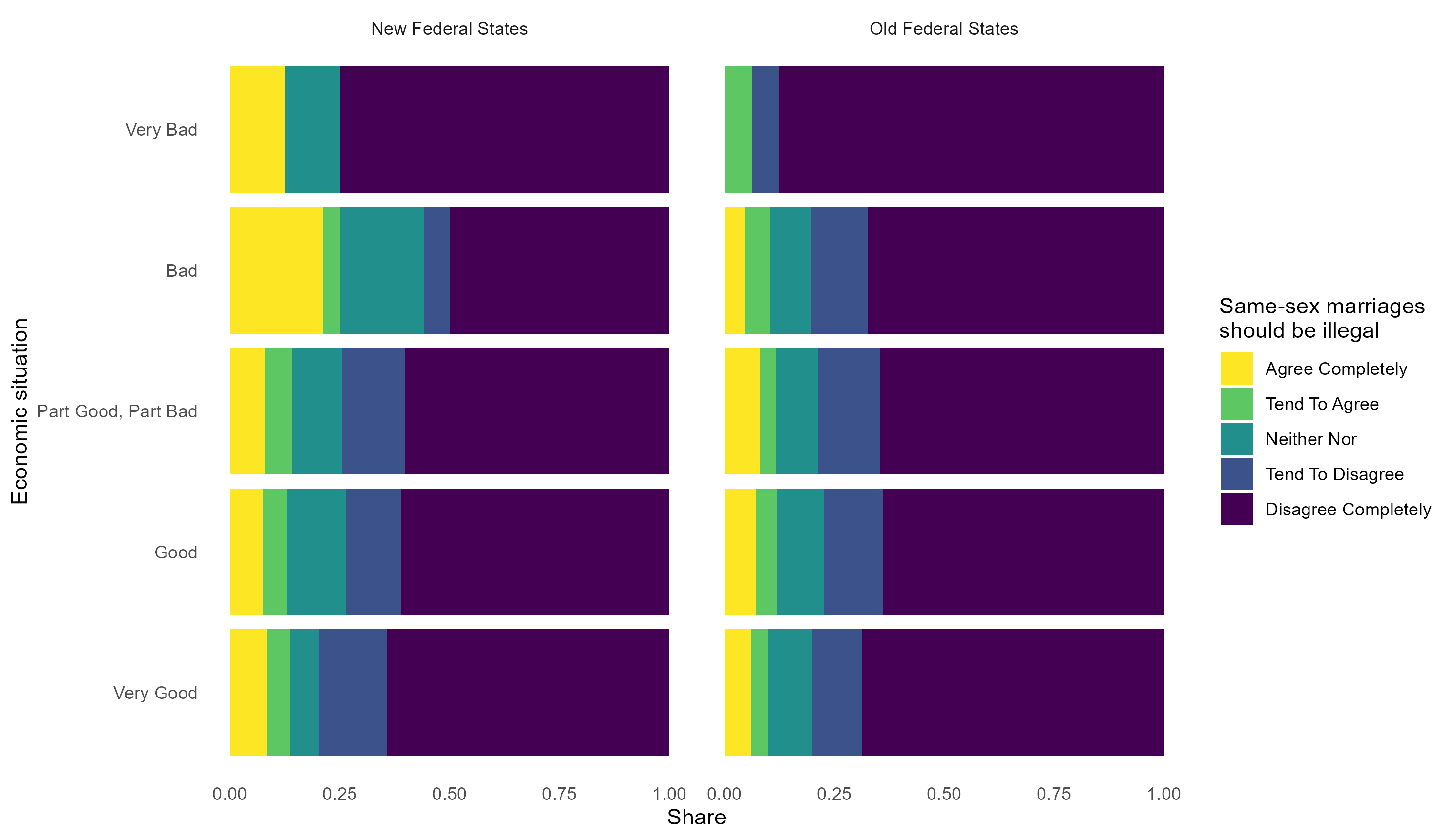
ggplot(allbus_data, aes(economic_situation)) +
geom_bar(
aes(fill = samesex_marriage),
position = position_fill(reverse = TRUE)
) +
facet_wrap(~eastwest) +
scale_fill_viridis_d(
name = "Same-sex marriages\nshould be illegal",
labels = str_to_title,
direction = -1
) +
scale_x_discrete(labels = str_to_title) +
coord_flip() +
theme_minimal() +
labs(x = "Economic situation", y = "Share") +
theme(panel.grid = element_blank())